Happy Monday! ☀️
Welcome to the 434 new hungry minds who have joined us since last Monday!
If you aren't subscribed yet, join smart, curious, and hungry folks by subscribing here.

📚 Software Engineering Articles
Inside Amazon's rigorous bar raiser interview process
Master these 12 OOP concepts to level up your coding
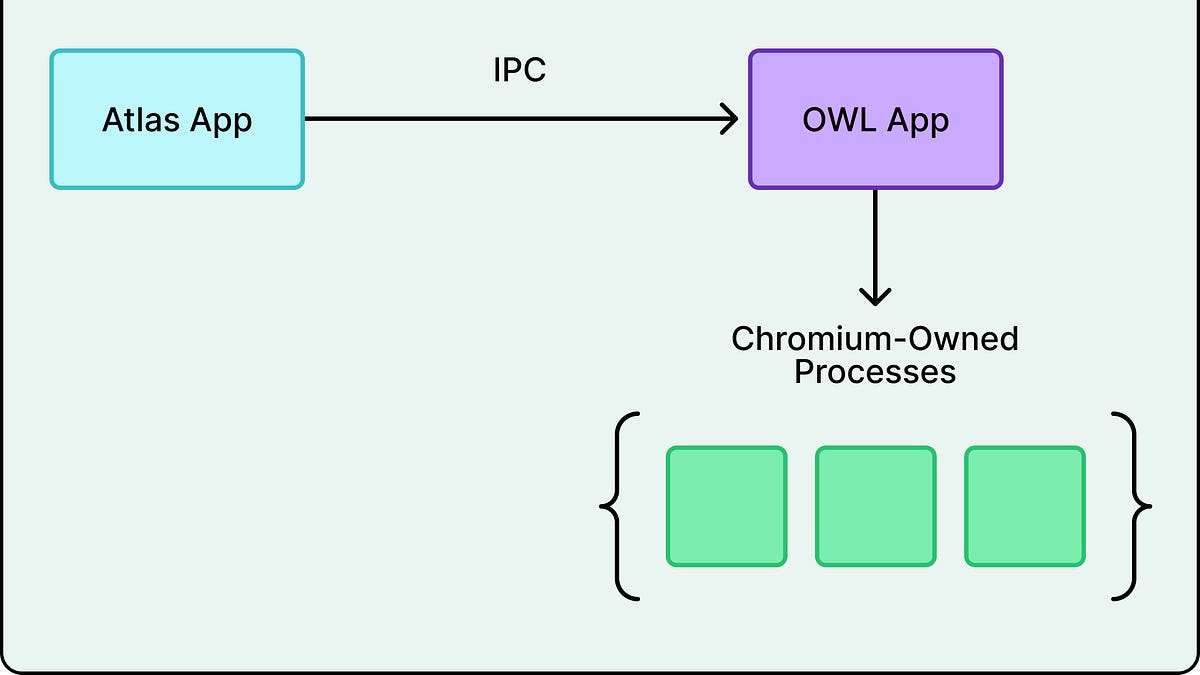
Deep dive into OpenAI's Atlas architecture powering the ChatGPT browser
Decode Yelp's AI assistant implementation from scratch
An ex-Googler shares 14 career lessons learned
🗞️ Tech and AI Trends
Two AI user types emerge, creating a surprising divide
How Apple's E-cores revolutionize chip performance
GLM-5 release shifts from vibe coding to engineering
👨🏻💻 Coding Tip
Configure Kafka's idempotent producers correctly to prevent message duplication
Time-to-digest: 5 minutes

Ever wondered how tech giants handle millions of API requests without breaking a sweat? Let's dive into building a distributed rate limiting system that can handle massive scale while maintaining precise request control across global data centers.
The challenge: Design a rate limiter that maintains consistency across multiple data centers while handling millions of requests per second with sub-millisecond latency.
Implementation highlights:
Redis-based token bucket: Implement sliding window rate limiting using Redis for atomic operations and high performance
Global synchronization: Use consistent hashing to distribute rate limit buckets across multiple Redis clusters
Circuit breakers: Gracefully handle Redis failures with local in-memory fallbacks to prevent cascade failures
Adaptive limits: Dynamic rate limit adjustments based on system load and user prioritization
Cached decisions: Implement local LRU caches to reduce Redis hits for frequently accessed limits
Results and learnings:
High performance: Achieved <1ms p99 latency for rate limit checks
Battle-tested: Successfully handles 5M+ requests/second across 3 global regions
Resource efficient: Reduced Redis CPU usage by 60% through smart caching
Building a distributed rate limiter teaches us that even seemingly simple concepts like "X requests per minute" become fascinating engineering challenges at scale. The key is finding the right balance between consistency, performance, and operational simplicity.

ESSENTIAL (read or not read, that's the question)
In defense of not reading the code
ARTICLE (chrome's new toy)
Chrome 146 includes an early preview of WebMCP
ARTICLE (yelp's AI waiter)
How Yelp Built "Yelp Assistant"
ESSENTIAL (googler's wisdom dump)
14 More lessons from 14 years at Google
ARTICLE (AI bestie story)
My AI adoption journey
ARTICLE (when AI meets real life chaos)
Coding Agents Meet Distributed Reality
ARTICLE (claude's coding sidekick)
How I Use Claude Code
ESSENTIAL (code review zen)
The PERFECT code review
ESSENTIAL (function calls aren't free lunch)
The cost of a function call
ARTICLE (roadmap to gaming roads)
Art of roads in games
Want to reach 200,000+ engineers?
Let’s work together! Whether it’s your product, service, or event, we’d love to help you connect with this awesome community.

Brief: Study reveals stark contrast between enterprise users limited to basic Microsoft Copilot and "power users" leveraging advanced tools like Claude Code, highlighting how corporate IT policies may be creating competitive disadvantages for larger companies against more AI-agile smaller firms.
Brief: Apple Silicon's efficiency cores handle background processes at lower frequencies while keeping P-cores free for user tasks, enabling better performance and power efficiency through smart Quality of Service management.
Brief: In a head-to-head comparison, Anthropic's Opus 4.6 leads in usability and broad adoption potential, while OpenAI's Codex 5.3 shows superior coding capabilities, marking a shift away from benchmark-based evaluations towards real-world performance in the AI coding assistant space.
Brief: A deep dive into using AI for debugging a Next.js React app reveals that while AI excels at common issues like schema validation, it struggles with complex problems requiring system understanding, achieving only partial success across three bug investigations.
Brief: Z.ai unveils GLM-5, a 744B parameter AI model featuring improved pre-training and reinforcement learning, achieving top performance in open-source benchmarks for reasoning and coding tasks, while offering support for multiple coding agents and local deployment options.

This week’s tip:
Kafka's idempotent producers automatically handle duplicate messages during retries by assigning sequence numbers, but require careful configuration of max.in.flight.requests.per.connection to maintain ordering guarantees. Setting it too high can cause out-of-order delivery even with idempotency enabled.

Wen?
Financial transactions: Preventing duplicate payments during network issues or broker restarts
Event sourcing systems: Ensuring state machines don't process the same event twice
High-throughput pipelines: Balancing performance with ordering when some reordering is acceptable
It takes half your life before you discover life is a do-it-yourself project. Napoleon Hill


That’s it for today! ☀️
Enjoyed this issue? Send it to your friends here to sign up, or share it on Twitter!
If you want to submit a section to the newsletter or tell us what you think about today’s issue, reply to this email or DM me on Twitter! 🐦
Thanks for spending part of your Monday morning with Hungry Minds.
See you in a week — Alex.
Icons by Icons8.
*I may earn a commission if you get a subscription through the links marked with “aff.” (at no extra cost to you).